BSBESB302 Develop and present business proposals
In this unit you will learn how to;
- Evaluate business ideas
- Manage risks associated with business proposals
- Develop proposals for viable business ideas
- Present the business proposal
Introduction
In unit BSBSTR301 Contribute to Continuous Improvement we discussed the reasons for change within a business;
“No organisation, large or small, can open its doors on day one and start to do business. Before operations can begin, a great deal of research and preparation needs to take place in order for the business to run smoothly and efficiently. Procedures and policies must be put in place so that the organisation has structure. It is to be hoped that these would be flexible enough to allow for growth and changes in trends.
Flexibility is a key element in the continued success of any business. While a set of policies and procedures are an excellent source of guidance on business operations, they should be flexible enough to allow for changes and improvements when called for.Coordinating, and managing improvements to a business is about a well researched and thought out, step by step approach to introducing something new to the company.
Issues when considering a change include;
- Where you are now?
- Where do you want to be in the future?
- How are you going to get there?
Answers to such questions, and managing change effectively is about thoroughly understanding your business and the industry that it is in.”
Continuous improvement in business processes is the basis for making changes; identifying opportunities or areas of the business that could be better. Equally, you may have an idea for introducing a completely new idea into the organisation, or starting up and entirely new business venture altogether.
And this is where developing business proposals can be useful – if not essential.
A business proposal is, at it’s core, a detailed report on;
- the idea for consideration;
- how does it fit within the organisational structure and/or vision?
- what benefits will it bring to the organisation?
- who is the target audience? … and so on.
- the resources required to develop the idea into a business practice, including financial, human and physical resources
- a risk assessment that outlines and addresses any threats, objections or obstacles that may prevent the idea from becoming a reality
- a plan of action that outlines developmental milestones such as the time frames and individual tasks required to bring the proposal from idea to reality.
Answering these questions, and looking at the issues, in advance of actually implementing any changes, can avoid costly mistakes and circumvent risks that might have been foreseen – had they been considered and planned for. As the saying goes: “failing to plan, is planning to fail”
Evaluating business ideas
Whether you are considering the development of a brand new venture, or looking at making an improvement in an existing one, research and planning are essential. You, or your organisation, may be spending considerable time, effort, resources and money on a business idea so you need to make sure it is feasible.
Key requirements in developing business proposals
In any case, there are a range of issues to bear in mind when developing and evaluating ideas; issues that may affect the way an idea is introduced into the organisation and the impact it may have on specific sectors or work practices.
Some of the key requirements in developing business proposals, then, may be to consider;
- organisational policies and procedures. Whenever any changes or suggestions are to be made you will always need to keep the organisations policies and procedures in mind. For example;
- in any instance where staffing is involved you will need to bear diversity and equal opportunity legislation in mind.
- any suggestions you make should be in line with the organisation’s mission or visions statement; enhancing their reputation and standing within their community.
- ensuring that workplace health and safety procedures are not compromised by the proposal.
- ensuring that organisational standards for quality are not compromised
- policies and procedures that revolve around;
- the quality of the products and/or services offered
- customer service standards
- workplace sustainability and so on….
- legislative requirements, regulations, standards and codes or practice such as;
- Industry regulations. Many industries have specific regulations, that apply to business practices within that industry, and that must be complied with by law. For example;
- businesses that service alcohol require a liquor licence, so this must be considered when developing a proposal for hospitality or bar operations.
- the building and construction industry has aNational Construction Code which provides strict guidelines that must be complied with. These must be considered when making any changes or developing business proposals.
- financial services businesses may be regulated by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority(APRA), that supervises the dealing across the banking, insurance and superannuation industries.
- Industry regulations. Many industries have specific regulations, that apply to business practices within that industry, and that must be complied with by law. For example;
- more on this in the learner guide ….
These, and other industry specific, issues must be taken into account when evaluating ideas and developing business proposals to ensure compliance with not only legal obligations, but to safeguard and enhance the organisation’s reputation.
Identifying ideas relating to business opportunities
Bearing the above in mind you can begin to identify ideas that may be of benefit to the organisation. You can do this by thoroughly examining the business environment in which you operate and undertaking an internal Audit and a SWOT Analysis.
Internal Audit
An internal audit involves taking an in depth look at how your business is currently functioning in order to determine where gaps may exist, or where the business is not performing as well as it should. Questions to be asked might include (but are not limited to);
- current business operations. These might involve such things as;
- resources at your disposal to carry out the work that needs to be done (or that a new idea might require). Resources can be staff, physical items such as machinery, office equipment, finances and so on. The availability of these resources will influence whether your idea is practical, or not. You may need to employ additional staff, train existing staff, purchase office equipment or borrow funds to develop and initiate the idea.You will then need to determine if the cost of implementing the idea is worth the cost.
- retooling – will your business idea require a major change in operations or new manufacturing equipment and machinery to be installed? This could mean substantial capital investment;
- making sure the business premises have the capacity to hold new machinery,
- ensuring all legal obligations will be met in introducing the new venture
- ensuring staff are properly trained in the use of this equipment
- market trends – is there enough interest, within your current customer community, to warrant making the necessary changes? If not, how will you reach new markets
- a realistic look at what business you are actually in;
- What is your core business?
- What is the business objective and/or mission?
- Is the business currently fulfilling this objective or mission?
- Who are you actually selling to?
- Are there any supplementary or complementary products that could be added to your current offerings?
- If so, will you need to “re-tool” or bring in additional or new resources?
- Is the idea for adding more products worth the expense of bringing in additional resources?
- How are you currently marketing your business?
- Are your products and services selling as well as they should? If not; why not?
- Can you improve your reach by using other marketing methods? Which ones?
- Are your employees working as efficiently as they could be?
- Are they being kept up to date on organisational plans and activities?
- Do they hold the necessary qualifications or experience to do their job?
- Is training required?
- Are you using technology as efficiently as possible?
- Do you have the equipment, software and applications necessary to function in an online business environment?
- Do you use social media as effectively as you could?
- Does your software capture the necessary information; allowing you to track your performance over time? … and so on.
These, along with many other in depth questions will give you a solid overview of the organisation’s current plans, capabilities and processes.
The SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis allows you to have a deep down, honest look at your organisation in terms of its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats and to determine ways to make improvements or to further expose any gaps in your current operations.
An example of a simple SWOT Analysis might look like this;
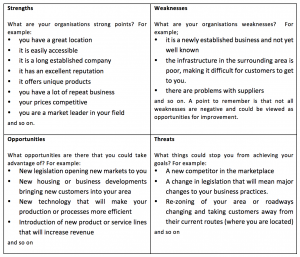
In examining your SWOT Analysis you can pinpoint areas that need to be addressed;
- Strengths – what can you do to capitalise or maximise on them?
- Weaknesses – what can you do to minimise or negate their impact. Which of them can be turned around to become a strength?
- Opportunities – what do you need to do to take advantage of these opportunities? How can you ensure you get your slice of this opportunity?
- Threats – what can you do to avoid or minimise the impact of the threat?
The answers to these questions form part of your research for a well thought out business proposal.
Researching the key factors that influence the viability of an idea
While ideas for business improvement or expansion might be exciting and creative, they may not necessarily be practical or financially viable. There is little point in implementing a new business idea if the cost of doing so outweighs its benefits.
In the ongoing process of researching your business idea there are a number of key factors that influence the viability of your proposal. These might include;
- personal circumstances and suitability of your own skills. Do you have the necessary experience or expertise to develop and implement your proposed idea? You may be put in a position of responsibility to drive your idea forward; from initial proposal through development and then implementation. This will only happen successfully if you have the necessary skill base to understand and communicate, to others, what needs to be done.
- risk assessment. What might the risks associated with this idea be, and how will you overcome them? We will look at this in more detail as we move through the unit.
- External business influences, such as PLESCT Analysis.
PLESCT Analysis
A PLESCT Analysis can be undertaken to take a thorough look at the external world around you and the influences various issues may have upon your business and industry as a whole.
PLESCT stands for: Political, Legislative, Economic, Social, Competitor and Technology and looks at each of these sectors and how they may affect you positively – or negatively.
A PLESCT Analysis, then, considers;
Political issues.
Here you should look at the general political stability of your country or state – or perhaps the international political environment.
- Is there an election due? People get nervous around election times and are cautious about spending / investing their money
- Has there just been an election? In which case is the new government likely to make changes to the status quo – and if so, how will this affect you?
- International economic and social environment; how stable is the situation?
- Is there likely to be any fallout, from international issues, for your local environment?
and so on….
For example, changes in government often have an impact on businesses dealing with health, education and employment as existing programs are often changed or discontinued after an election, or new programs are introduced. International economic crises often have a significant impact on our own market, as does the increasing threat of terrorism or conflict situations. So, too, do global pandemics and the risk of associated health issues.
Legislative or other legal issues
Legislative issues often bring compliance requirements with them; requirements that you are legally bound by. Questions that will need to be answered might include;
…. continued in the learner guide….
For purchase information go back to the Business resources page
